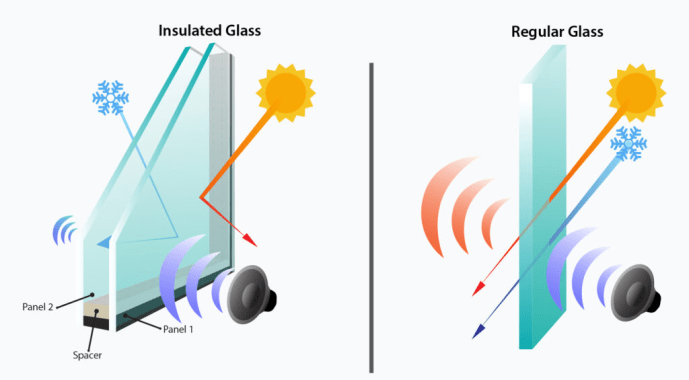
An insulated glass unit (IGU) consists of multiple glass panes separated by air or a noble gas-filled cavity that reduces heat transfer and provides building insulation. Insulated glass significantly regulates the indoor temperature and acts as a barrier to unwanted heat and noise.
This article discusses the components, working, and features of insulated glass in building construction.
Components of Insulated Glass Unit (IGU)
The major components of insulated glass are:
- Desiccant: It is a drying agent used in IG to remove humidity and moisture present in between the glass panes. The most commonly used desiccants in insulated glass are silica and zeolites.
- Spacer: The spacer determines the width of the gap between the two panes of glass in an insulated glass unit (IGU). It provides a fixed gap between two layers of glass and is made of aluminum or thermoplastic material. Desiccant rests between the spacers.
- Sealants: Sealants are applied on IGU to make sure the insulated air doesn’t escape from the cavity. The most common sealant used in IGU units is butyl sealant.
- Cavity: The insulation characteristics of IG are due to the air or gas-filled cavity. Air is commonly used in the cavity of double glazing glass. Argos, krypton, or other gases that slow the transfer of heat are also used to fill the cavity.
Features of Insulated Glass Units (IGUs)
- IGUs prevent heat loss through the glass doors and windows. The gas layer in the cavity forms the insulation layer that diffuses heat transfer.
- IGUs provide increased strength for residential, commercial, and industrial structural glazing units. High-strength IGUs are more durable, resilient, and secure.
- The multiple layers of glass panes in an IGU boost the overall strength against extreme wind forces and severe weather conditions.
- IGUs can be single seal units and double seal units. The former has a single seal between the spacer and glass, while the latter has a double seal.
- Based on the type of glass used for panes, it can be tempered glass, low-E glass, tempered glass, etc.
- Insulating glass is a form of thermal insulation that reduces the load on heating and cooling equipment. They help achieve the desired indoor temperature without consuming excessive power and energy. This, hence, reduces energy cost, and carbon emission and forms an eco-friendly glazing option.
- IGUs permit the construction of visually impressive glass facades for building structures.
FAQs
An insulated glass unit (IGU) is a glass unit that consists of multiple glass panes separated by air or a noble gas-filled cavity that reduces heat transfer and provides building insulation.
IGUs prevent heat loss through the glass doors and windows. The gas layer in the cavity forms the insulation layer that diffuses heat transfer.
Insulating glass is a form of thermal insulation that reduces the load on heating and cooling equipment. They help achieve the desired indoor temperature without consuming excessive power and energy. This, hence, reduces energy cost, and carbon emission and forms an eco-friendly glazing option.
Read More